Your Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors images are available in this site. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors files here. Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for listeria monocytogenes virulence factors images information related to the listeria monocytogenes virulence factors topic, you have come to the right site. Our site always provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Listeria Monocytogenes Virulence Factors. Monocytogenes major virulence factor. Monocytogenes are highly regulated and tightly controlled. It is a facultative intracellular and Gram-positive bacterium presented in pregnant women by flu-like symptoms 1 - 3. It is the major virulence factor of L.
 Virulence Factors That Modulate The Cell Biology Of Listeria Infection And The Host Response Sciencedirect From sciencedirect.com
Virulence Factors That Modulate The Cell Biology Of Listeria Infection And The Host Response Sciencedirect From sciencedirect.com
The gram-positive pathogenic bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is widely spread in the nature. These factors include for example Lap protein Listeria adhesion protein which promotes bacterial paracellular translocation through cell junctions during the gastrointestinal stage of infection Kim and Bhunia 2013. It is a food-borne pathogen responsible for listeriosis one of the deadliest foodborne infections known today. Monocytogenes major virulence factor. Listeriosis mostly affects pregnant. Listeriolysin O LLO is a L.
Monocytogenes was reported to be isolated from soil water sewage and sludge.
Listeria monocytogenes Virulence Factors. It is the major virulence factor of L. It helps cell to cell spread of the bacteria by dissolving cell membrane. These factors include for example Lap protein Listeria adhesion protein which promotes bacterial paracellular translocation through cell junctions during the gastrointestinal stage of infection Kim and Bhunia 2013. Monocytogenes major virulence factor. The transition between saprophytic and pathogenic life is mediated through complex regulatory pathways that modulate the expression of virulence factors.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The food-borne pathogen Listeria monocytogenesis adapted to a diversity of environments such as soil food body fluids and the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors are secreted in biologically active Extracellular Vesicles Carolina Coelho Lisa Brown Maria Maryam Meagan C. These factors include for example Lap protein Listeria adhesion protein which promotes bacterial paracellular translocation through cell junctions during the gastrointestinal stage of infection Kim and Bhunia 2013. Virulence mechanisms in L. SUMMARY The gram-positive bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of listeriosis a highly fatal opportunistic foodborne infection.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Monocytogenes is accomplished through invasion from cell-to-cell. The spread of L. Listeria monocytogenes a bacterium that causes foodborne infections can result in abortion and diseases as severe as encephalomeningitis septicemias and gastroenteritis. A number of virulence factors that play important roles in pathogenesis of listeriosis have been identified and characterized. Kyle Heino M.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Monocytogenes major virulence factor. Our knowledge regarding the role of these foods in L. A number of virulence factors that play important roles in pathogenesis of listeriosis have been identified and characterized. Listeriosis mostly affects pregnant. Coelho C Brown L Maryam M Vij R Smith DFQ Burnet MC et al.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular pathogen that is able to adhere to invade and survive within mammalian cells including macrophages. Various produce including cantaloupe caramel-coated apples and packaged salads have been recognized in recent years as vehicles for listeriosis a human foodborne disease caused by intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. It is the major virulence factor of L. It has the ability to escape host defense mechanisms and causes listeriosis more frequently in immunocompromised individuals. In the course of infection in mammals LLO is required for intracellular survival and apoptosis induction in lymphocytes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Monocytogenes was reported to be isolated from soil water sewage and sludge. Nakayasu Nathan Ryan Brady Anne Hamacher-Brady. Listeriolysin O LLO is a L. Various produce including cantaloupe caramel-coated apples and packaged salads have been recognized in recent years as vehicles for listeriosis a human foodborne disease caused by intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Monocytogenes virulence however is limited.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The food-borne pathogen Listeria monocytogenesis adapted to a diversity of environments such as soil food body fluids and the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. It has the ability to escape host defense mechanisms and causes listeriosis more frequently in immunocompromised individuals. The food-borne pathogen Listeria monocytogenesis adapted to a diversity of environments such as soil food body fluids and the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. It is a food-borne pathogen responsible for listeriosis one of the deadliest foodborne infections known today. It helps cell to cell spread of the bacteria by dissolving cell membrane.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
SUMMARY The gram-positive bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of listeriosis a highly fatal opportunistic foodborne infection. Safety and immunogenicity of listeria monocytogenes were related to its virulence genes. The danger of food contamination as a result of the bacterium in the refrigeration process have drawn attention to the study of virulence factors associated with L. The food-borne pathogen Listeria monocytogenesis adapted to a diversity of environments such as soil food body fluids and the cytosol of eukaryotic cells. These factors include for example Lap protein Listeria adhesion protein which promotes bacterial paracellular translocation through cell junctions during the gastrointestinal stage of infection Kim and Bhunia 2013.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular pathogen that is able to adhere to invade and survive within mammalian cells including macrophages. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors including listeriolysin O are secreted in biologically active extracellular vesicles. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors including listeriolysin O are secreted in biologically active extracellular vesicles. Monocytogenes is accomplished through invasion from cell-to-cell. The transition between saprophytic and pathogenic life is mediated through complex regulatory pathways that modulate the expression of virulence factors.
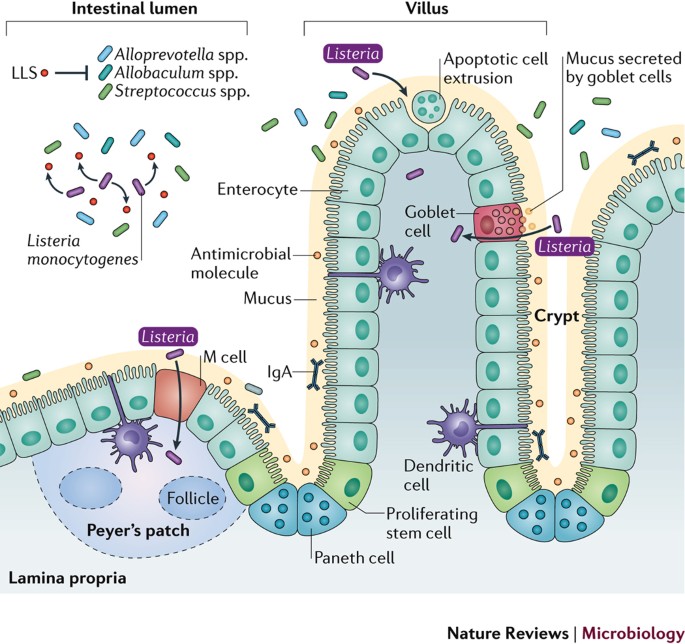 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
Listeriolysin O LLO is a L. The development of infection depends on several factors which includes host susceptibility gastric acidity inoculum size and virulence factor of the bacteria. It helps cell to cell spread of the bacteria by dissolving cell membrane. It is a food-borne pathogen responsible for listeriosis one of the deadliest foodborne infections known today. Listeriosis mostly affects pregnant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Monocytogenes was reported to be isolated from soil water sewage and sludge. The possibility that a number of other factors may be involved in L. Listeriolysin O LLO is a L. Kyle Heino M. Monocytogenes is in the host activation of the central virulence regulatory protein PrfA leads to increased expression of several secreted virulence factors as well as PrsA2 which is required for the folding and stability of listeriolysin LLO the Mpl protease that activates the broad-range phospholipase PlcB ActA and other factors.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The development of infection depends on several factors which includes host susceptibility gastric acidity inoculum size and virulence factor of the bacteria. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors including listeriolysin O are secreted in biologically active extracellular vesicles. The gram-positive pathogenic bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is widely spread in the nature. Pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes. SUMMARY The gram-positive bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of listeriosis a highly fatal opportunistic foodborne infection.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
Virulence mechanisms in L. SUMMARY The gram-positive bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of listeriosis a highly fatal opportunistic foodborne infection. It is a food-borne pathogen responsible for listeriosis one of the deadliest foodborne infections known today. The development of infection depends on several factors which includes host susceptibility gastric acidity inoculum size and virulence factor of the bacteria. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors including listeriolysin O are secreted in biologically active extracellular vesicles J Biol Chem.
Source: journals.plos.org
Listeria monocytogenes a bacterium that causes foodborne infections can result in abortion and diseases as severe as encephalomeningitis septicemias and gastroenteritis. Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative intracellular pathogen that is able to adhere to invade and survive within mammalian cells including macrophages. The transition between saprophytic and pathogenic life is mediated through complex regulatory pathways that modulate the expression of virulence factors. Clinical manifestations of invasive listeriosis are usually. Safety and immunogenicity of listeria monocytogenes were related to its virulence genes.
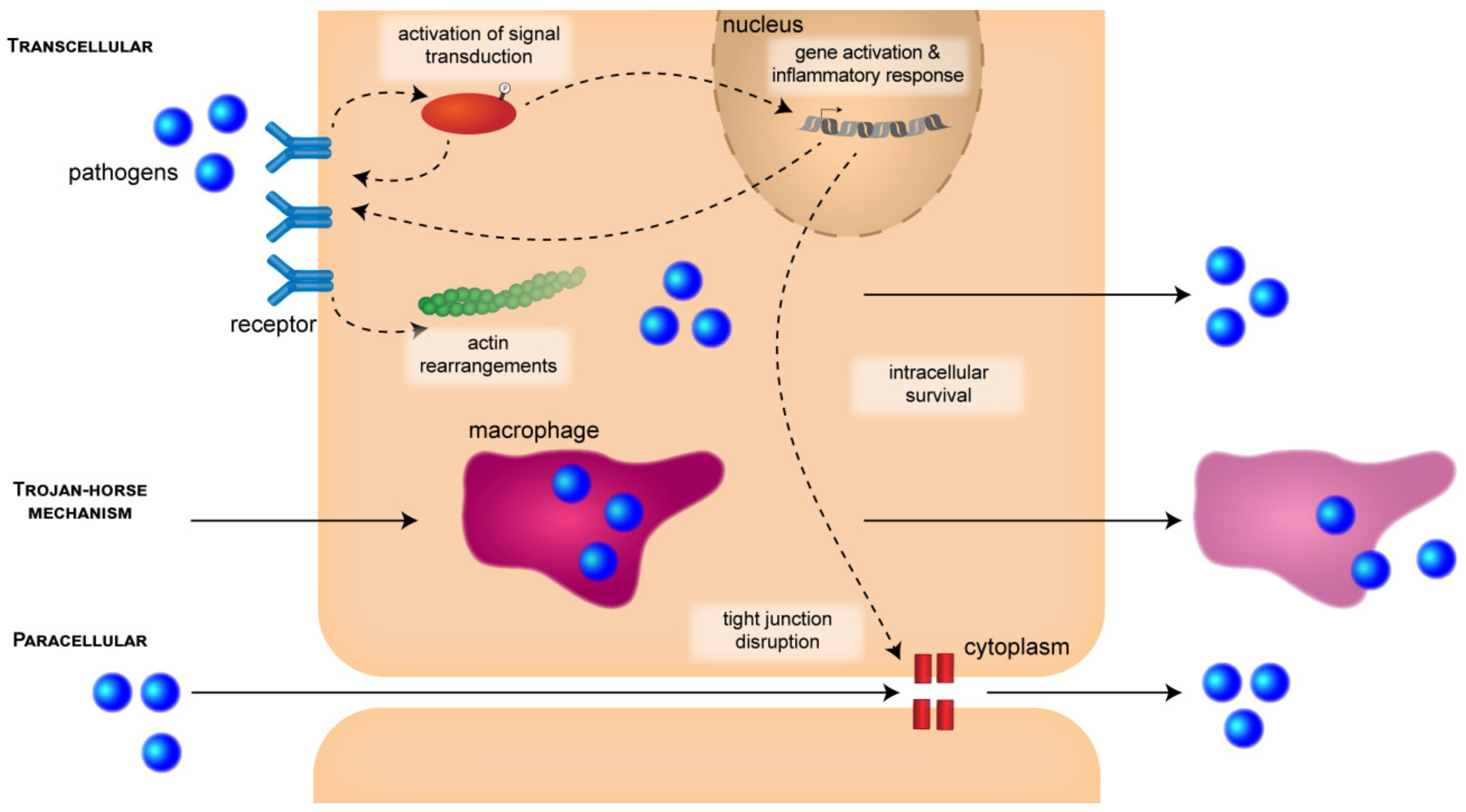 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
It helps cell to cell spread of the bacteria by dissolving cell membrane. Monocytogenes is in the host activation of the central virulence regulatory protein PrfA leads to increased expression of several secreted virulence factors as well as PrsA2 which is required for the folding and stability of listeriolysin LLO the Mpl protease that activates the broad-range phospholipase PlcB ActA and other factors. Listeria monocytogenes a bacterium that causes foodborne infections can result in abortion and diseases as severe as encephalomeningitis septicemias and gastroenteritis. Listeriolysin O LLO is a L. Pathogenesis of Listeria monocytogenes.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Various produce including cantaloupe caramel-coated apples and packaged salads have been recognized in recent years as vehicles for listeriosis a human foodborne disease caused by intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Monocytogenes invasion also needs to be given consideration. Listeria monocytogenes bile salt hydrolase is a PrfA-regulated virulence factor involved in the intestinal and hepatic phases of listeriosis. The possibility that a number of other factors may be involved in L. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors are secreted in biologically active Extracellular Vesicles Carolina Coelho Lisa Brown Maria Maryam Meagan C.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Monocytogenes virulence however is limited. Listeria monocytogenes bile salt hydrolase is a PrfA-regulated virulence factor involved in the intestinal and hepatic phases of listeriosis. Monocytogenes are highly regulated and tightly controlled. SUMMARY The gram-positive bacterium Listeria monocytogenes is the causative agent of listeriosis a highly fatal opportunistic foodborne infection. Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors including listeriolysin O are secreted in biologically active extracellular vesicles.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Listeria monocytogenes virulence factors including listeriolysin O are secreted in biologically active extracellular vesicles. Listeria monocytogenes a bacterium that causes foodborne infections can result in abortion and diseases as severe as encephalomeningitis septicemias and gastroenteritis. The transition between saprophytic and pathogenic life is mediated through complex regulatory pathways that modulate the expression of virulence factors. Monocytogenes is in the host activation of the central virulence regulatory protein PrfA leads to increased expression of several secreted virulence factors as well as PrsA2 which is required for the folding and stability of listeriolysin LLO the Mpl protease that activates the broad-range phospholipase PlcB ActA and other factors. It is a facultative intracellular and Gram-positive bacterium presented in pregnant women by flu-like symptoms 1 - 3.
 Source: microbeonline.com
Source: microbeonline.com
Monocytogenes is accomplished through invasion from cell-to-cell. Burnet Jennifer E. It is a food-borne pathogen responsible for listeriosis one of the deadliest foodborne infections known today. Pregnant women neonates the elderly and debilitated or immunocompromised patients in general are predominantly affected although the disease can also develop in normal individuals. Monocytogenes is accomplished through invasion from cell-to-cell.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title listeria monocytogenes virulence factors by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






