Your Locally competitive algorithm images are ready. Locally competitive algorithm are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Locally competitive algorithm files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for locally competitive algorithm pictures information linked to the locally competitive algorithm interest, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
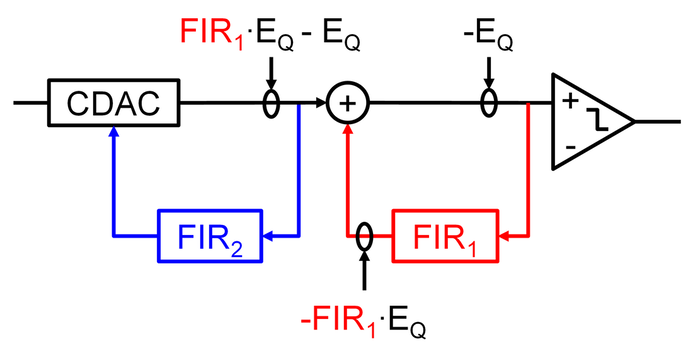
Locally Competitive Algorithm. LCAs are designed to be implemented in a dynamical system composed of many neuron-like elements operating in parallel. The network itself lacks much of the anatomical structure we see in real brains but it does include lateral connectivity and iterative or recurrent computation. From a Locally Competitive Algorithm to Sensory Relevance Models. Shapero et al 2014.
 Petavision From petavision.github.io
Petavision From petavision.github.io
From a Locally Competitive Algorithm to Sensory Relevance Models. Locally Competitive Algorithm Sparse Approximation - raintwotoLCAjl. TeuscherLab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University Portland OR USA. This approach allows us to model informative global features resulting from both photoelectric absorption and Compton. Convergence of the algorithm to the correct solution is theoretically proven and guaranteed Balavoine et al 2012 2013a b. A Causal Locally Competitive Algorithm for the Sparse Decomposition of Audio Signals Adam Charles Abbie Kressner Christopher Rozell Georgia Institute of.
SLCA first layer neurons are derived from locally competitive algorithms which produce responses and learn representations that are well.
We introduce subspace locally competitive algorithms SLCAs a family of novel network architectures for modeling latent repre-sentations of natural signals with group sparse structure. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA Rozell et al 2008 is a biologically plausible algorithm that solves the sparse approximation problem. Walt Woods and Christof Teuscher. A Causal Locally Competitive Algorithm for the Sparse Decomposition of Audio Signals Adam Charles Abbie Kressner Christopher Rozell Georgia Institute of. Locally Competitive Algorithm Sparse Approximation - raintwotoLCAjl. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a biologically plausible computational architecture for sparse coding where a signal is represented as a linear combination of elements from an over-complete dictionary.
Source:
Locally Competitive Algorithms LCAs each dictionary element is assigned to a node that may continually compete with neighboring nodes. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals. We introduce subspace locally competitive algorithms SLCAs a family of novel network architectures for modeling latent repre-sentations of natural signals with group sparse structure. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under award 1028378 and by. 1 Abstract Analysis and applications of the Locally Competitive Algorithm by Dylan M Paiton Doctor of Philosophy in Vision Science University of California Berkeley Professor Bruno Olshausen Chair The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals.
Source:
I Since the sparsity-inducing function is not differentiable motivated by the concept of locally competitive algorithm LCA we combine LCA and alternating direction method of multipliers ADMM to devise a fast and accurate algorithm to solve the general nonsmooth sparse approximation problems. Locally Competitive Algorithm Sparse Approximation - raintwotoLCAjl. LCAs are designed to be implemented in a dynamical system composed of many neuron-like elements operating in parallel. Walt Woods and Christof Teuscher. A Causal Locally Competitive Algorithm for the Sparse Decomposition of Audio Signals Adam Charles Abbie Kressner Christopher Rozell Georgia Institute of.
Source:
These systems use thresholding functions to induce. 1 Abstract Analysis and applications of the Locally Competitive Algorithm by Dylan M Paiton Doctor of Philosophy in Vision Science University of California Berkeley Professor Bruno Olshausen Chair The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals. We present a class of locally competitive algorithms LCAs that correspond to a collection of sparse approximation principles minimizing a weighted combination of reconstruction MSE and a coefficient cost function. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a biologically plausible computational architecture for sparse coding where a signal is represented as a linear combination of elements from an over-complete dictionary. The network itself lacks much of the anatomical structure we see in real brains but it does include lateral connectivity and iterative or recurrent computation.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a biologically plausible computational architecture for sparse coding where a signal is represented as a linear combination of elements from an over-complete dictionary. Locally Competitive Algorithm Sparse Approximation - raintwotoLCAjl. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under award 1028378 and by. We introduce subspace locally competitive algorithms SLCAs a family of novel network architectures for modeling latent representations of natural signals with group sparse structure. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals.
 Source: mpflynngroup.com
Source: mpflynngroup.com
LOCALLY COMPETITIVE ALGORITHM S FOR SPARSE APPROXIMATION Christopher Rozell Don Johnson Richard Baraniuk Electrical Computer Engi neering Department Rice University Bruno Olshausen Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute University of California Berkeley ABSTRACT Practicalsparse approximation al gorithms particularly greedy algo-. For more details see. I Since the sparsity-inducing function is not differentiable motivated by the concept of locally competitive algorithm LCA we combine LCA and alternating direction method of multipliers ADMM to devise a fast and accurate algorithm to solve the general nonsmooth sparse approximation problems. This approach allows us to model informative global features resulting from both photoelectric absorption and Compton. TeuscherLab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University Portland OR USA.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Shapero et al 2014. From a Locally Competitive Algorithm to Sensory Relevance Models. This approach allows us to model informative global features resulting from both photoelectric absorption and Compton. For more details see. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals.
Source: researchgate.net
This project is a bare bones implementation of LCAs sparse approximation algorithm. The network itself lacks much of the anatomical structure we see in real brains but it does include lateral connectivity and iterative or recurrent computation. Rozell Christopher and Johnson Don and Baraniuk Richard and Olshausen Bruno Locally competitive algorithms for sparse approximation IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2007. Locally Competitive Algorithms LCAs each dictionary element is assigned to a node that may continually compete with neighboring nodes. For more details see.
 Source: petavision.github.io
Source: petavision.github.io
TeuscherLab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University Portland OR USA. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals. Locally Competitive Algorithms LCAs each dictionary element is assigned to a node that may continually compete with neighboring nodes. Locally competitive algorithms Rozell Johnson Baraniuk Olshausen 2007 are dynamic models that are implementable in hardware and converge to good solutions for sparse approximation. LOCALLY COMPETITIVE ALGORITHM S FOR SPARSE APPROXIMATION Christopher Rozell Don Johnson Richard Baraniuk Electrical Computer Engi neering Department Rice University Bruno Olshausen Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute University of California Berkeley ABSTRACT Practicalsparse approximation al gorithms particularly greedy algo-.
Source:
Locally Competitive Algorithms LCAs each dictionary element is assigned to a node that may continually compete with neighboring nodes. For more details see. This project is a bare bones implementation of LCAs sparse approximation algorithm. This approach allows us to model informative global features resulting from both photoelectric absorption and Compton. 1 Abstract Analysis and applications of the Locally Competitive Algorithm by Dylan M Paiton Doctor of Philosophy in Vision Science University of California Berkeley Professor Bruno Olshausen Chair The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals.
 Source: dl.acm.org
Source: dl.acm.org
The network itself lacks much of the anatomical structure we see in real brains but it does include lateral connectivity and iterative or recurrent computation. I Since the sparsity-inducing function is not differentiable motivated by the concept of locally competitive algorithm LCA we combine LCA and alternating direction method of multipliers ADMM to devise a fast and accurate algorithm to solve the general nonsmooth sparse approximation problems. We present a class of locally competitive algorithms LCAs that correspond to a collection of sparse approximation principles minimizing a weighted combination of reconstruction MSE and a coefficient cost function. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a recurrent neural network for performing sparse coding and dictionary learning of natural signals. The network itself lacks much of the anatomical structure we see in real brains but it does include lateral connectivity and iterative or recurrent computation.
Source:
The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a biologically plausible computational architecture for sparse coding where a signal is represented as a linear combination of elements from an over-complete dictionary. SLCA first layer neurons are derived from locally competitive algorithms which produce responses and learn representations that are well. We briefly summarize the contributions of this work as follows. Shapero et al 2014. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA Rozell et al 2008 is a biologically plausible algorithm that solves the sparse approximation problem.
 Source: dlacombejr.github.io
Source: dlacombejr.github.io
We introduce subspace locally competitive algorithms SLCAs a family of novel network architectures for modeling latent representations of natural signals with group sparse structure. Utilizing the output of a traditional gamma-ray detector our spiking locally competitive algorithm uses sparse coding optimization to compare global patterns in a gamma-ray spectrum with a dictionary of radionuclide templates. Rozell Christopher and Johnson Don and Baraniuk Richard and Olshausen Bruno Locally competitive algorithms for sparse approximation IEEE International Conference on Image Processing 2007. LOCALLY COMPETITIVE ALGORITHM S FOR SPARSE APPROXIMATION Christopher Rozell Don Johnson Richard Baraniuk Electrical Computer Engi neering Department Rice University Bruno Olshausen Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute University of California Berkeley ABSTRACT Practicalsparse approximation al gorithms particularly greedy algo-. These systems use thresholding functions to induce.
 Source: dlacombejr.github.io
Source: dlacombejr.github.io
Unlike greedy algorithms that irrevocably select. TeuscherLab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University Portland OR USA. This project is a bare bones implementation of LCAs sparse approximation algorithm. These systems use thresholding functions to induce. Utilizing the output of a traditional gamma-ray detector our spiking locally competitive algorithm uses sparse coding optimization to compare global patterns in a gamma-ray spectrum with a dictionary of radionuclide templates.
Source:
Walt Woods and Christof Teuscher. In these models each unit has an state and when presented with a stimulus each unit begins accumulating activity that leaks out over time much like a bucket with small holes on the bottom. I Since the sparsity-inducing function is not differentiable motivated by the concept of locally competitive algorithm LCA we combine LCA and alternating direction method of multipliers ADMM to devise a fast and accurate algorithm to solve the general nonsmooth sparse approximation problems. Unlike greedy algorithms that irrevocably select. Convergence of the algorithm to the correct solution is theoretically proven and guaranteed Balavoine et al 2012 2013a b.
Source:
Locally Competitive Algorithm Sparse Approximation - raintwotoLCAjl. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA Rozell et al 2008 is a biologically plausible algorithm that solves the sparse approximation problem. This project is a bare bones implementation of LCAs sparse approximation algorithm. We introduce subspace locally competitive algorithms SLCAs a family of novel network architectures for modeling latent representations of natural signals with group sparse structure. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under award 1028378 and by.
Source:
The network itself lacks much of the anatomical structure we see in real brains but it does include lateral connectivity and iterative or recurrent computation. I Since the sparsity-inducing function is not differentiable motivated by the concept of locally competitive algorithm LCA we combine LCA and alternating direction method of multipliers ADMM to devise a fast and accurate algorithm to solve the general nonsmooth sparse approximation problems. Node dynamics are described by a set of non-linear ordinary differential equations ODEs that correspond to simple analog hard-ware components. TeuscherLab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Portland State University Portland OR USA. Convergence of the algorithm to the correct solution is theoretically proven and guaranteed Balavoine et al 2012 2013a b.
Source:
LOCALLY COMPETITIVE ALGORITHM S FOR SPARSE APPROXIMATION Christopher Rozell Don Johnson Richard Baraniuk Electrical Computer Engi neering Department Rice University Bruno Olshausen Helen Wills Neuroscience Institute University of California Berkeley ABSTRACT Practicalsparse approximation al gorithms particularly greedy algo-. Locally competitive algorithms LCA are continuous Hop eld-like networks for which the optimization problems of sparse representation are weak Lyapunov functions. I Since the sparsity-inducing function is not differentiable motivated by the concept of locally competitive algorithm LCA we combine LCA and alternating direction method of multipliers ADMM to devise a fast and accurate algorithm to solve the general nonsmooth sparse approximation problems. Node dynamics are described by a set of non-linear ordinary differential equations ODEs that correspond to simple analog hard-ware components. Unlike greedy algorithms that irrevocably select.
Source:
In these models each unit has an state and when presented with a stimulus each unit begins accumulating activity that leaks out over time much like a bucket with small holes on the bottom. The Locally Competitive Algorithm LCA is a continuous-time dynamical system designed to solve the problem of sparse approximation. For more details see. Locally competitive algorithms Rozell Johnson Baraniuk Olshausen 2007 are dynamic models that are implementable in hardware and converge to good solutions for sparse approximation. Locally competitive algorithms LCA are continuous Hop eld-like networks for which the optimization problems of sparse representation are weak Lyapunov functions.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title locally competitive algorithm by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






