Your Mutualism parasitism continuum images are ready. Mutualism parasitism continuum are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Mutualism parasitism continuum files here. Download all free images.
If you’re searching for mutualism parasitism continuum pictures information connected with to the mutualism parasitism continuum topic, you have come to the right site. Our website always gives you suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Mutualism Parasitism Continuum. In a classic example rhizobia fix atmospheric nitrogen for legume hosts in exchange for photosynthetic carbon. Title Functioning of mycorrhizal associations along the mutualism-parasitism continuum abstract A great diversity of plants and fungi engage in mycorrhizal associations. EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002. By Ann M Hirsch.
 Pdf Functioning Of Mycorrhizas Along The Mutualism Parasitism Continuum From researchgate.net
Pdf Functioning Of Mycorrhizas Along The Mutualism Parasitism Continuum From researchgate.net
Septate endophyte colonization and host responses of grasses and forbs native to a tallgrass prairie. It reviewed all classes of mycorrhiza. The mutualism-parasitism continuum As had been done by Francis and Read 1995 Johnson et al. Parasitism- Refers to a type of symbiotic relationship where only one is benefited while the other is harmed. The model includes both benefits and costs to the interaction and spans the mutualismparasitism continuum. Variation in the functioning of mutualisms caused by context dependency has important ecological conse-.
EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002.
EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002. Specifically this approach suggests that symbionts with mobile life history stages should evolve toward extremely severe parasitism vector-borne symbionts should evolve toward severe parasitism in vertebrate hosts and benign parasitism in the vectors waterborne symbionts should evolve toward severe parasitism symbionts transmitted by predation should evolve toward severe parasitism in prey hosts and benign parasitism. Deciphering Evolutionary Mechanisms Between Mutualistic and Pathogenic Symbioses. We focused on interactions with the pathogen Bacillus thuringiensis. In natural habitats and in an ecologically meaningful time span these associations have evolved to improve the fitness of both plant and fungal symbionts. Context dependency is deemed to position the outcomes of species interactions along a continuum of mutualism to parasitism.
 Source: encyclopedie-environnement.org
Source: encyclopedie-environnement.org
Symbioses are modelled as evolutionarily and ecologically variable with fitness outcomes for hosts shifting on a continuum from mutualism to parasitism. Deciphering Evolutionary Mechanisms Between Mutualistic and Pathogenic Symbioses. Specifically this approach suggests that symbionts with mobile life history stages should evolve toward extremely severe parasitism vector-borne symbionts should evolve toward severe parasitism in vertebrate hosts and benign parasitism in the vectors waterborne symbionts should evolve toward severe parasitism symbionts transmitted by predation should evolve toward severe parasitism in prey hosts and benign parasitism. Parasitism can be developmentally induced environmentally induced or possibly genotypically induced. But exclusively vertical transmission can.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Deciphering Evolutionary Mechanisms Between Mutualistic and Pathogenic Symbioses. On the mutualism-parasitism continuum Johnson et al. Transmission Modes and Evolution of the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum a. The mutualismparasitism continuum of Bradyrhizobium and iii discern whether host control occurs over initial nodule formation or via modulation of nodule metabo-lism and growth. Mutualisms involving symbiont inheritance are predicted to be stable on the continuum and unlikely to revert to parasitism 1597.
 Source: sfamjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: sfamjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Search for more papers by this author. In soils of high fertility the net benefit a fungus confers to a plant is. A continuum from commensalism to parasitism. EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002. The mutualismparasitism continuum of Bradyrhizobium and iii discern whether host control occurs over initial nodule formation or via modulation of nodule metabo-lism and growth.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Transmission Modes and Evolution of the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum a. The mutualism-parasitism continuum As had been done by Francis and Read 1995 Johnson et al. But exclusively vertical transmission can. Variation in the functioning of mutualisms caused by context dependency has important ecological conse-. To determine the factors predicting the outcome of interspecific interac-tions along this continuum requires an understanding of the spatial temporal and taxonomic context for a given system Herre et al.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Deciphering Evolutionary Mechanisms Between Mutualistic and Pathogenic Symbioses. Transmission Modes and Evolution of the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum a. Parasitism- Refers to a type of symbiotic relationship where only one is benefited while the other is harmed. In a classic example rhizobia fix atmospheric nitrogen for legume hosts in exchange for photosynthetic carbon. Context dependency is deemed to position the outcomes of species interactions along a continuum of mutualism to parasitism.
 Source: cambridge.org
Source: cambridge.org
But exclusively vertical transmission can. Materials and methods Bradyrhizobium inocula Four Bradyrhizobium genotypes referred to as s 2 14. The mutualism-parasitism continuum As had been done by Francis and Read 1995 Johnson et al. Continuum of mutualism to parasitism. But exclusively vertical transmission can.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
In natural habitats and in an ecologically meaningful time span these associations have evolved to improve the fitness of both plant and fungal symbionts. Selection for parasitism led to symbionts increasing pathogen-induced mortality but reduced their competitive ability with pathogens and their in vitro growth rates. The model includes both benefits and costs to the interaction and spans the mutualismparasitism continuum. On the mutualism-parasitism continuum Johnson et al. Transmission Modes and Evolution of the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum a.
 Source: encyclopedie-environnement.org
Source: encyclopedie-environnement.org
On the mutualism-parasitism continuum Johnson et al. The mutualism-parasitism-continuum is a. We focused on interactions with the pathogen Bacillus thuringiensis. In a classic example rhizobia fix atmospheric nitrogen for legume hosts in exchange for photosynthetic carbon. EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002.
 Source: yaledailynews.com
Source: yaledailynews.com
The mutualismparasitism continuum of Bradyrhizobium and iii discern whether host control occurs over initial nodule formation or via modulation of nodule metabo-lism and growth. 1997 put together the spectrum of responses to AM colonization in terms of a mutualism-parasitism continuum of mycorrhizal functioning. To determine the factors predicting the outcome of interspecific interac-tions along this continuum requires an understanding of the spatial temporal and taxonomic context for a given system Herre et al. EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002. Septate endophyte colonization and host responses of grasses and forbs native to a tallgrass prairie.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
By Ann M Hirsch. Mycorrhizal fungi might be considered to be parasitic on plants when net cost of the symbiosis exceeds net benefits. ContinuumRefers to a type of symbiotic relationship where only one is benefited while the other species is neither harmed nor benefited. But exclusively vertical transmission can. Septate endophyte colonization and host responses of grasses and forbs native to a tallgrass prairie.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In systems managed by humans mycorrhizal associations often improve plant productivity but this is not always the case. The model includes both benefits and costs to the interaction and spans the mutualismparasitism continuum. Symbioses are modelled as evolutionarily and ecologically variable with fitness outcomes for hosts shifting on a continuum from mutualism to parasitism. ContinuumRefers to a type of symbiotic relationship where only one is benefited while the other species is neither harmed nor benefited. Specifically this approach suggests that symbionts with mobile life history stages should evolve toward extremely severe parasitism vector-borne symbionts should evolve toward severe parasitism in vertebrate hosts and benign parasitism in the vectors waterborne symbionts should evolve toward severe parasitism symbionts transmitted by predation should evolve toward severe parasitism in prey hosts and benign parasitism.
 Source: cambridge.org
Source: cambridge.org
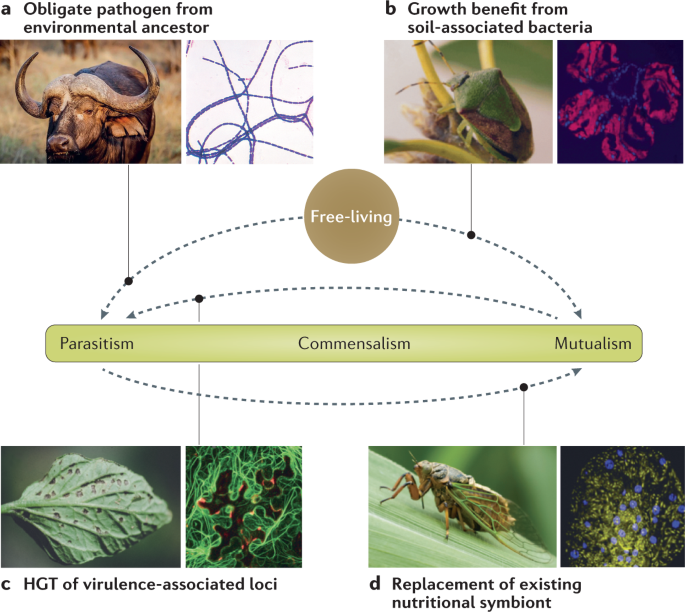
Selecting for parasitism in terms of facilitating pathogen infection or increased mutualism in terms of host protection. Mutualismâparasitism paradigm synthesized from results of root-endophyte models. A continuum from commensalism to parasitism. Continuum of mutualism to parasitism. Transmission Modes and Evolution of the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum a.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Context dependency is deemed to position the outcomes of species interactions along a continuum of mutualism to parasitism. The mutualism-parasitism continuum As had been done by Francis and Read 1995 Johnson et al. Transmission Modes and Evolution of the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum a. ContinuumRefers to a type of symbiotic relationship where only one is benefited while the other species is neither harmed nor benefited. Symbioses are modelled as evolutionarily and ecologically variable with fitness outcomes for hosts shifting on a continuum from mutualism to parasitism.
 Source: cambridge.org
Source: cambridge.org
The mutualism-parasitism-continuum is a. In a classic example rhizobia fix atmospheric nitrogen for legume hosts in exchange for photosynthetic carbon. A continuum from commensalism to parasitism. Deciphering Evolutionary Mechanisms Between Mutualistic and Pathogenic Symbioses. The mutualismparasitism continuum of Bradyrhizobium and iii discern whether host control occurs over initial nodule formation or via modulation of nodule metabo-lism and growth.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The mutualism-parasitism continuum As had been done by Francis and Read 1995 Johnson et al. A continuum from commensalism to parasitism. The mutualismparasitism continuum of Bradyrhizobium and iii discern whether host control occurs over initial nodule formation or via modulation of nodule metabo-lism and growth. The model includes both benefits and costs to the interaction and spans the mutualismparasitism continuum. Mutualismâparasitism paradigm synthesized from results of root-endophyte models.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
EWALD Department of Biology Amherst College Amherst Massachusetts 01002. The mutualism-parasitism continuum As had been done by Francis and Read 1995 Johnson et al. The mutualism-parasitism-continuum is a. Materials and methods Bradyrhizobium inocula Four Bradyrhizobium genotypes referred to as s 2 14. Thus it is imperative to understand which factors determine where a particular interspecific interaction falls along the continuum.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
Selection for parasitism led to symbionts increasing pathogen-induced mortality but reduced their competitive ability with pathogens and their in vitro growth rates. Deciphering Evolutionary Mechanisms Between Mutualistic and Pathogenic Symbioses. Continuum of mutualism to parasitism. Mutualismâparasitism paradigm synthesized from results of root-endophyte models. 1997 put together the spectrum of responses to AM colonization in terms of a mutualism-parasitism continuum of mycorrhizal functioning.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Research on mycorrhizal fungi has been pivotal in developing an understanding of the variability in presumed mutualisms Sapp 2004. Research on mycorrhizal fungi has been pivotal in developing an understanding of the variability in presumed mutualisms Sapp 2004. Symbioses are modelled as evolutionarily and ecologically variable with fitness outcomes for hosts shifting on a continuum from mutualism to parasitism. Search for more papers by this author. Context dependency is deemed to position the outcomes of species interactions along a continuum of mutualism to parasitism.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title mutualism parasitism continuum by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





