Your N glycolyl neuraminic acid images are available. N glycolyl neuraminic acid are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the N glycolyl neuraminic acid files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re searching for n glycolyl neuraminic acid pictures information connected with to the n glycolyl neuraminic acid keyword, you have come to the right blog. Our website always gives you suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
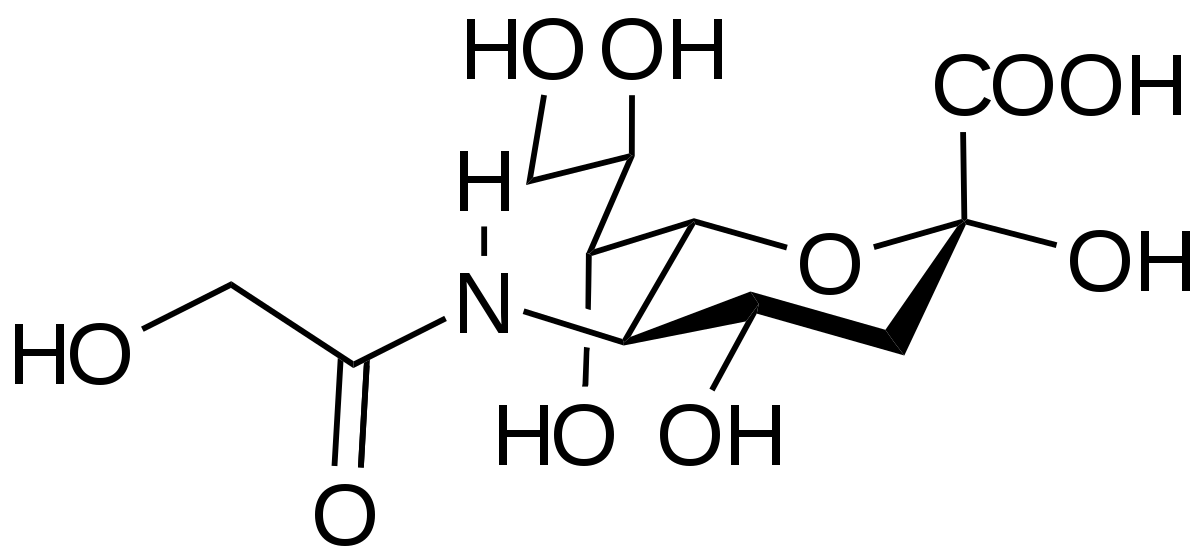
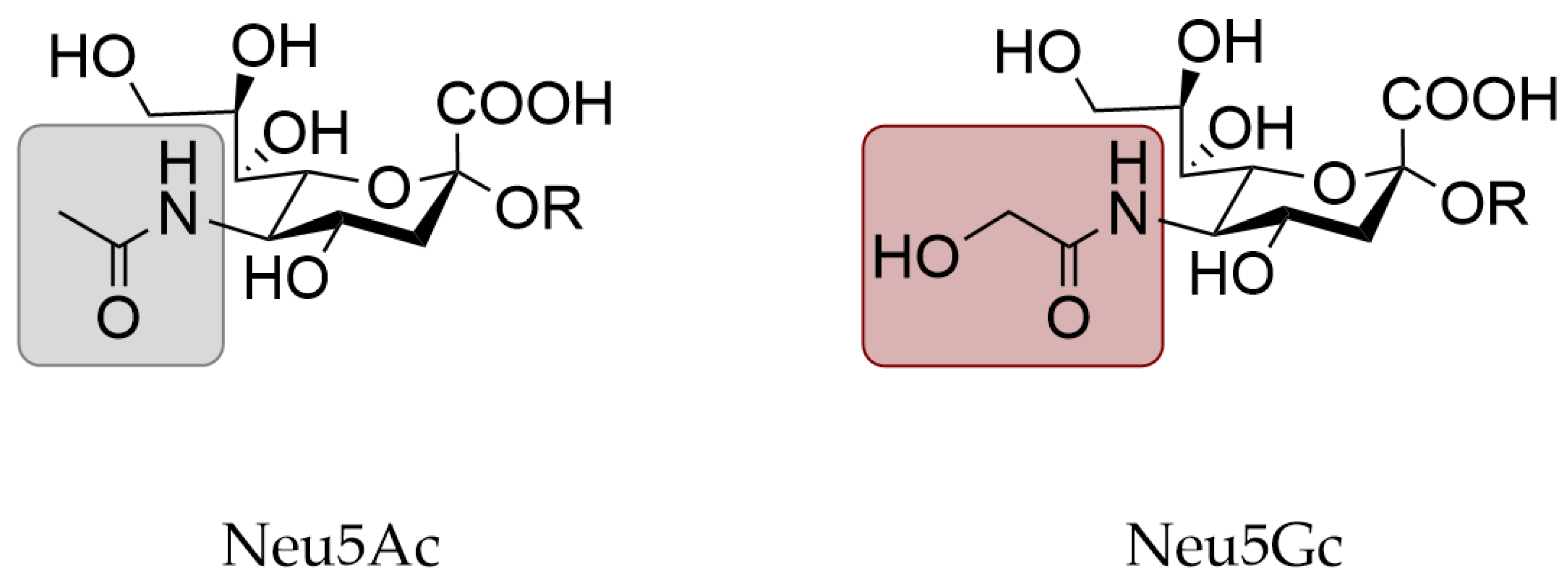
N Glycolyl Neuraminic Acid. An N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. Influenza D virus diverges from its related influenza C virus in the recognition of 9-O-acetylated N-acetyl- or N-glycolyl-neuraminic acid-containing glycan receptors. One major modification at C-5 is N-glycolyl NeuGc instead of N-acetyl NeuAc. In humans due to deletion of the gene for the hydroxylase enzyme N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc is absent.
Plos One Healthy Human Serum N Glycan Profiling Reveals The Influence Of Ethnic Variation On The Identified Cancer Relevant Glycan Biomarkers From journals.plos.org
6000 3600 You save 2400 Write a Review Write a Review. BIOSYNTHESIS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID. Catalyzes the activation of N-acetylneuraminic acid NeuNAc to cytidine 5-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid CMP-NeuNAc a substrate required for the addition of sialic acid. In addition to N-acetylneuraminic acid Neu5Ac N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc is among the most common sialic acid forms in nature. N-Glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc is a sialic acid that is found in non-human primate tissues. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I.
12 It is not endogenously produced in humans due to a mutation in the gene that encodes CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase the enzyme that hydrolyzes N-acetylneuraminic acid to form Neu5Gc but accumulates in human cells after exogenous ingestion from dietary sources such as red meat and dairy products.
One major modification at C-5 is N-glycolyl NeuGc instead of N-acetyl NeuAc. The two most common sialic acids found in mammals are N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-glycolylhydroxyl acetic acidneuraminic acid Figure 87. IMPORTANCEThe most common sialic acid in humans is 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid Neu5Ac but various modifications give rise to more than 50 different sialic acid variants that decorate the cell surface. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. N-glycoloyl-beta-neuraminic acid is an N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. BIOSYNTHESIS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
6000 3600 You save 2400 Write a Review Write a Review. An N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. In addition to N-acetylneuraminic acid Neu5Ac N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc is among the most common sialic acid forms in nature. Influenza D virus IDV utilizes bovines as a primary reservoir with periodical spillover to other mammalian hosts. It is a conjugate acid of a N-glycoloylneuraminate.
 Source: commons.wikimedia.org
Source: commons.wikimedia.org
One major modification at C-5 is N-glycolyl NeuGc instead of N-acetyl NeuAc. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I. 12 It is not endogenously produced in humans due to a mutation in the gene that encodes CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase the enzyme that hydrolyzes N-acetylneuraminic acid to form Neu5Gc but accumulates in human cells after exogenous ingestion from dietary sources such as red meat and dairy products. It has a role as a mammalian metabolite and an antigen. These glycolyl groups are derived from acetyl groups by enzymic oxidation.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
BIOSYNTHESIS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. BIOSYNTHESIS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID. 6000 3600 You save 2400 Write a Review Write a Review. N-glycolyl is mammalian specific and expressed in pigs and horses but not in humans ferrets seals or dogs.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
These glycolyl groups are derived from acetyl groups by enzymic oxidation. These glycolyl groups are derived from acetyl groups by enzymic oxidation. Influenza D virus diverges from its related influenza C virus in the recognition of 9-O-acetylated N-acetyl- or N-glycolyl-neuraminic acid-containing glycan receptors. In addition to N-acetylneuraminic acid Neu5Ac N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc is among the most common sialic acid forms in nature. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN.
Source: commons.wikimedia.org
NeuGc-binding viruses are perfectly viable and neuraminidases can cleave NeuGc-containing receptor structuresThere is anapparentselection now for NeuAc as no. N-Glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc is a sialic acid that is found in non-human primate tissues. It is a conjugate acid of a N-glycoloylneuraminate. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. However Neu5Gc is found in foods derived from poultry fish red meat and milk products and has been shown to be metabolically.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Influenza D virus IDV utilizes bovines as a primary reservoir with periodical spillover to other mammalian hosts. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I. 6000 3600 You save 2400 Write a Review Write a Review. One major modification at C-5 is N-glycolyl NeuGc instead of N-acetyl NeuAc. NeuGc-binding viruses are perfectly viable and neuraminidases can cleave NeuGc-containing receptor structuresThere is anapparentselection now for NeuAc as no.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The B subunit of the subtilase cytotoxin SubB produced by Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli recognises Neu5Gc containing glycans. 6000 3600 You save 2400 Write a Review Write a Review. It has a role as a mammalian metabolite and an antigen. N-Glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc is a sialic acid that is found in non-human primate tissues. IMPORTANCEThe most common sialic acid in humans is 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid Neu5Ac but various modifications give rise to more than 50 different sialic acid variants that decorate the cell surface.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Catalyzes the activation of N-acetylneuraminic acid NeuNAc to cytidine 5-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid CMP-NeuNAc a substrate required for the addition of sialic acid. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I. IMPORTANCEThe most common sialic acid in humans is 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid Neu5Ac but various modifications give rise to more than 50 different sialic acid variants that decorate the cell surface. It is a conjugate acid of a N-glycoloylneuraminate. Influenza D virus IDV utilizes bovines as a primary reservoir with periodical spillover to other mammalian hosts.
 Source: sigmaaldrich.com
Source: sigmaaldrich.com
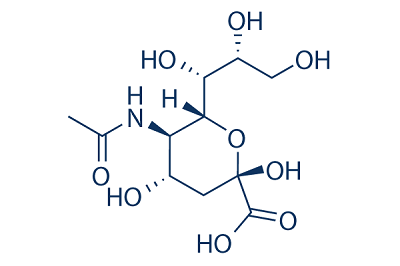
N-glycoloylneuraminic acid is a N-acylneuraminic acid. Unlike most mammals humans cannot synthesize the sialic acid variant 5-N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc due to a gene defect. 12 It is not endogenously produced in humans due to a mutation in the gene that encodes CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase the enzyme that hydrolyzes N-acetylneuraminic acid to form Neu5Gc but accumulates in human cells after exogenous ingestion from dietary sources such as red meat and dairy products. In addition to N-acetylneuraminic acid Neu5Ac N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc is among the most common sialic acid forms in nature. N-Glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc is a sialic acid that is found in non-human primate tissues.
 Source: commons.wikimedia.org
Source: commons.wikimedia.org
The B subunit of the subtilase cytotoxin SubB produced by Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli recognises Neu5Gc containing glycans. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. Influenza D virus IDV utilizes bovines as a primary reservoir with periodical spillover to other mammalian hosts. Sialic acids constitute a family of negatively charged structurally diverse monosaccharides that are commonly presented on the termini of glycans in higher animals and some microorganisms. N-glycolyl is mammalian specific and expressed in pigs and horses but not in humans ferrets seals or dogs.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
6000 3600 You save 2400 Write a Review Write a Review. Influenza D virus IDV utilizes bovines as a primary reservoir with periodical spillover to other mammalian hosts. The two most common sialic acids found in mammals are N-acetylneuraminic acid and N-glycolylhydroxyl acetic acidneuraminic acid Figure 87. It has a role as a mammalian metabolite and an antigen. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I.
 Source: cymitquimica.com
Source: cymitquimica.com
N-glycolyl is mammalian specific and expressed in pigs and horses but not in humans ferrets seals or dogs. N-glycoloyl-beta-neuraminic acid is an N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. BIOSYNTHESIS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID. N-glycoloylneuraminic acid is a N-acylneuraminic acid. An N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc-containing glycans are a prominent form of aberrant glycosylation found in human tumor cells and have been proposed as cancer biomarkers. The B subunit of the subtilase cytotoxin SubB produced by Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli recognises Neu5Gc containing glycans. N-Glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc is a sialic acid that is found in non-human primate tissues. An N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. N-glycoloylneuraminic acid is a N-acylneuraminic acid.
Source: journals.plos.org
Influenza D virus diverges from its related influenza C virus in the recognition of 9-O-acetylated N-acetyl- or N-glycolyl-neuraminic acid-containing glycan receptors. These glycolyl groups are derived from acetyl groups by enzymic oxidation. However Neu5Gc is found in foods derived from poultry fish red meat and milk products and has been shown to be metabolically. IMPORTANCEThe most common sialic acid in humans is 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid Neu5Ac but various modifications give rise to more than 50 different sialic acid variants that decorate the cell surface. N-glycoloylneuraminic acid is a N-acylneuraminic acid.
 Source: tcichemicals.com
Source: tcichemicals.com
Unlike most mammals humans cannot synthesize the sialic acid variant 5-N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc due to a gene defect. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. Influenza D virus diverges from its related influenza C virus in the recognition of 9-O-acetylated N-acetyl- or N-glycolyl-neuraminic acid-containing glycan receptors. N-glycoloyl-beta-neuraminic acid is an N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I.
 Source: qa-bio.com
Source: qa-bio.com
Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. In addition to N-acetylneuraminic acid Neu5Ac N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc is among the most common sialic acid forms in nature. BIOSYNTHESIS OF N-GLYCOLYLNEURAMINIC ACID. N-glycoloyl-beta-neuraminic acid is an N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre. An N-acylneuraminic acid in which the acyl substituent on nitrogen is glycolyl and which has beta-configuration at the anomeric centre.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
It has a role as a mammalian metabolite and an antigen. Unlike most mammals humans cannot synthesize the sialic acid variant 5-N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc due to a gene defect. 12 It is not endogenously produced in humans due to a mutation in the gene that encodes CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase the enzyme that hydrolyzes N-acetylneuraminic acid to form Neu5Gc but accumulates in human cells after exogenous ingestion from dietary sources such as red meat and dairy products. Has some activity toward NeuNAc N-glycolylneuraminic acid Neu5Gc or 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-nononic acid KDN. NeuGc-binding viruses are perfectly viable and neuraminidases can cleave NeuGc-containing receptor structuresThere is anapparentselection now for NeuAc as no.
 Source: nutraherbsource.com
Source: nutraherbsource.com
Unlike most mammals humans cannot synthesize the sialic acid variant 5-N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc due to a gene defect. N-acetyl or N-glycolyl neuraminic acid and they explain these specificities using X-ray structures. Up to now six neuraminic acid derivatives having glycolyl groups at either the amino or a hydroxyl group of the neuraminic acid molecule have been isolated from various animals and are numbered 3 and 11-15 in Table I. In addition to N-acetylneuraminic acid Neu5Ac N-glycolyl neuraminic acid Neu5Gc is among the most common sialic acid forms in nature. 12 It is not endogenously produced in humans due to a mutation in the gene that encodes CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase the enzyme that hydrolyzes N-acetylneuraminic acid to form Neu5Gc but accumulates in human cells after exogenous ingestion from dietary sources such as red meat and dairy products.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title n glycolyl neuraminic acid by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






