Your Presynaptic inhibition images are ready. Presynaptic inhibition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Presynaptic inhibition files here. Find and Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for presynaptic inhibition pictures information related to the presynaptic inhibition keyword, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site frequently gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Presynaptic Inhibition. Although the precise actions of. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry 49 937 944. Presynaptic inhibitors act as a high-pass filter but the functional consequence of this filtering du. Presynaptic inhibition is a significant synaptic event within the enteric microcircuits of the gastric corpus and antrum as well as the small and large intestine and rectum of the guinea pig190208209313314It is a mechanism that prevents runaway excitation in feed-forward synaptic circuits Figure 216.
 Image Result For Dextromethorphan Mechanism Of Action Pharmacology Brain Stem No Response From pinterest.com
Image Result For Dextromethorphan Mechanism Of Action Pharmacology Brain Stem No Response From pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition is a very powerful inhibitory mechanism and despite many detailed studies its purpose is still only partially understood. One accepted function is that by reducing afferent inflow to the spinal cord and brainstem the tonic level of presynaptic inhibition prevents sensory systems from being overloaded. Presynaptic inhibition is modulated by supraspinal centres and primary afferents in order to filter sensory information adjust spinal reflex excitability and ensure smooth movement. Presynaptic Inhibition and Neural Control Edited by Pablo Rudomin Ranulfo Romo and Lorne Mendell This is a timely review of the mechanisms underlying presynaptic control of synaptic transmission and the role they play in sensory and motor behavior. As a result the information flowing through sensory terminals can be modified before it reaches the target neurones through a process that can be controlled selectively by supraspinal centres to optimise motor performance and sensory. Presynaptic inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the lower limbs of subjects with upper motoneurone disease.
Presynaptic inhibition is a very powerful inhibitory mechanism and despite many detailed studies its purpose is still only partially understood.
Presynaptic inhibition is a widespread mechanism for regulating transmitter release in the CNS. Post-synaptic cells have mechanisms to communicate with the pre-synaptic cell and this can include inhibiting that cell. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry 49 937 944. In its most conventional form presynaptic inhibition involves axo-axonic synapses made by GABAergic interneurons 2. These results support the idea that in Aplysia presynaptic inhibition is caused primarily by a direct transmitter-mediated reduction in presynaptic Ca2 current and secondarily by a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic neuron due to a transmitter-mediated increase in a K currentABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS PMID. The amplitude of EPSPs in 15 soleus motoneurons was decreased by 5-84 with a mean inhibition.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic Inhibition is a mechanism by which the amount of neurotransmitter released by an individual synapse can be reduced resulting of less excitation of the post-synaptic neurone. After spinal cord injury SCI the supraspinal control of primary afferent depolarization PAD interneurons is disengaged suggesting an increased role for. When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input. In 33 MG cells PBST conditioning stimulation reduced the amplitude of EPSPs by 11-50 with a mean inhibition of 27. Presynaptic Inhibition and Neural Control Edited by Pablo Rudomin Ranulfo Romo and Lorne Mendell This is a timely review of the mechanisms underlying presynaptic control of synaptic transmission and the role they play in sensory and motor behavior.
 Source: fr.pinterest.com
Source: fr.pinterest.com
The synaptic efficacy of the afferent volleys entering the spinal cord can be modulated by presynaptic inhibition. Presynaptic inhibition by post-synaptic cells Although we think of neuronal signalling as one way thats not entirely true. A diminution in the effect of a presynaptic neuron on its postsynaptic neuron caused by a third neuron that makes an axoaxonic synapse with the presynaptic neuron near its terminal bouton. In its most conventional form presynaptic inhibition involves axo-axonic synapses made by GABAergic interneurons 2. Presynaptic Inhibition and Neural Control Edited by Pablo Rudomin Ranulfo Romo and Lorne Mendell This is a timely review of the mechanisms underlying presynaptic control of synaptic transmission and the role they play in sensory and motor behavior.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition is a widespread mechanism for regulating transmitter release in the CNS. These results support the idea that in Aplysia presynaptic inhibition is caused primarily by a direct transmitter-mediated reduction in presynaptic Ca2 current and secondarily by a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic neuron due to a transmitter-mediated increase in a K currentABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS PMID. Five decades ago it was reported that activation of afferent fibers originating in flexors led to depression of monosynaptic group Ia excitatory postsynaptic potentials EPSPs evoked on extensor motoneurones in the cat spinal cord. Presynaptic inhibition by post-synaptic cells Although we think of neuronal signalling as one way thats not entirely true. Presynaptic inhibition is a widespread mechanism for regulating transmitter release in the CNS.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry 49 937 944. At excitatory synapses activation of presynaptic GABA B receptors causes a reduction of neurotransmitter release 15 by inhibiting voltage-dependent Calcium channels 16 17. In 33 MG cells PBST conditioning stimulation reduced the amplitude of EPSPs by 11-50 with a mean inhibition of 27. When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input. The amplitude of EPSPs in 15 soleus motoneurons was decreased by 5-84 with a mean inhibition.
 Source: cz.pinterest.com
Source: cz.pinterest.com
One accepted function is that by reducing afferent inflow to the spinal cord and brainstem the tonic level of presynaptic inhibition prevents sensory systems from being overloaded. Presynaptic inhibition is modulated by supraspinal centres and primary afferents in order to filter sensory information adjust spinal reflex excitability and ensure smooth movement. In its most conventional form presynaptic inhibition involves axo-axonic synapses made by GABAergic interneurons 2. When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input. Presynaptic inhibition is a significant synaptic event within the enteric microcircuits of the gastric corpus and antrum as well as the small and large intestine and rectum of the guinea pig190208209313314It is a mechanism that prevents runaway excitation in feed-forward synaptic circuits Figure 216.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The synaptic efficacy of the afferent volleys entering the spinal cord can be modulated by presynaptic inhibition. After spinal cord injury SCI the supraspinal control of primary afferent depolarization PAD interneurons is disengaged suggesting an increased role for. Presynaptic inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the lower limbs of subjects with upper motoneurone disease. Although the precise actions of. These results support the idea that in Aplysia presynaptic inhibition is caused primarily by a direct transmitter-mediated reduction in presynaptic Ca2 current and secondarily by a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic neuron due to a transmitter-mediated increase in a K currentABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS PMID.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition is a very powerful inhibitory mechanism and despite many detailed studies its purpose is still only partially understood. When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry 49 937 944. Presynaptic inhibition is a very powerful inhibitory mechanism and despite many detailed studies its purpose is still only partially understood. A diminution in the effect of a presynaptic neuron on its postsynaptic neuron caused by a third neuron that makes an axoaxonic synapse with the presynaptic neuron near its terminal bouton.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
One accepted function is that by reducing afferent inflow to the spinal cord and brainstem the tonic level of presynaptic inhibition prevents sensory systems from being overloaded. The synaptic efficacy of the afferent volleys entering the spinal cord can be modulated by presynaptic inhibition. These results support the idea that in Aplysia presynaptic inhibition is caused primarily by a direct transmitter-mediated reduction in presynaptic Ca2 current and secondarily by a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic neuron due to a transmitter-mediated increase in a K currentABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS PMID. Of course related effects also occur at the network levelinhibiting an inhibitory neuron increases the net excitation in the population for both pre- and post-synaptic inhibition. Presynaptic Inhibition is a mechanism by which the amount of neurotransmitter released by an individual synapse can be reduced resulting of less excitation of the post-synaptic neurone.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Although the precise actions of. Although the precise actions of. Presynaptic inhibition of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 TRPV1 receptors by noradrenaline in nociceptive neurons. Presynaptic inhibition by post-synaptic cells Although we think of neuronal signalling as one way thats not entirely true. Presynaptic inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the lower limbs of subjects with upper motoneurone disease.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Although the precise actions of. In its most conventional form presynaptic inhibition involves axo-axonic synapses made by GABAergic interneurons 2. Presynaptic inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the lower limbs of subjects with upper motoneurone disease. Presynaptic inhibition by post-synaptic cells Although we think of neuronal signalling as one way thats not entirely true. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry 49 937 944.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition is a mechanism that suppresses synaptic transmission by means of presynaptic receptors and can occur through a variety of pathways 14. Presynaptic inhibition is a significant synaptic event within the enteric microcircuits of the gastric corpus and antrum as well as the small and large intestine and rectum of the guinea pig190208209313314It is a mechanism that prevents runaway excitation in feed-forward synaptic circuits Figure 216. Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry 49 937 944. These results support the idea that in Aplysia presynaptic inhibition is caused primarily by a direct transmitter-mediated reduction in presynaptic Ca2 current and secondarily by a hyperpolarization of the presynaptic neuron due to a transmitter-mediated increase in a K currentABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS PMID. When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Overview of Pre-synaptic inhibition and post-synaptic inhibition in the nervous system. As a result the information flowing through sensory terminals can be modified before it reaches the target neurones through a process that can be controlled selectively by supraspinal centres to optimise motor performance and sensory. Presynaptic inhibition is a very powerful inhibitory mechanism and despite many detailed studies its purpose is still only partially understood. Overview of Pre-synaptic inhibition and post-synaptic inhibition in the nervous system. In its most conventional form presynaptic inhibition involves axo-axonic synapses made by GABAergic interneurons 2.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition PSI refers to a decrease of transmitter release at central synapses. At excitatory synapses activation of presynaptic GABA B receptors causes a reduction of neurotransmitter release 15 by inhibiting voltage-dependent Calcium channels 16 17. As a result the information flowing through sensory terminals can be modified before it reaches the target neurones through a process that can be controlled selectively by supraspinal centres to optimise motor performance and sensory. One accepted function is that by reducing afferent inflow to the spinal cord and brainstem the tonic level of presynaptic inhibition prevents sensory systems from being overloaded. Presynaptic inhibition is a widespread mechanism for regulating transmitter release in the CNS.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A diminution in the effect of a presynaptic neuron on its postsynaptic neuron caused by a third neuron that makes an axoaxonic synapse with the presynaptic neuron near its terminal bouton. Presynaptic inhibition of monosynaptic reflexes in the lower limbs of subjects with upper motoneurone disease. Of course related effects also occur at the network levelinhibiting an inhibitory neuron increases the net excitation in the population for both pre- and post-synaptic inhibition. The synaptic efficacy of the afferent volleys entering the spinal cord can be modulated by presynaptic inhibition. Presynaptic inhibition is a widespread mechanism for regulating transmitter release in the CNS.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition is a widespread mechanism for regulating transmitter release in the CNS. Overview of Pre-synaptic inhibition and post-synaptic inhibition in the nervous system. One accepted function is that by reducing afferent inflow to the spinal cord and brainstem the tonic level of presynaptic inhibition prevents sensory systems from being overloaded. As a result the information flowing through sensory terminals can be modified before it reaches the target neurones through a process that can be controlled selectively by supraspinal centres to optimise motor performance and sensory. A diminution in the effect of a presynaptic neuron on its postsynaptic neuron caused by a third neuron that makes an axoaxonic synapse with the presynaptic neuron near its terminal bouton.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input. It involves binding of chemical messengers to inhibitory receptors at transmitter release sites on the axon. In 33 MG cells PBST conditioning stimulation reduced the amplitude of EPSPs by 11-50 with a mean inhibition of 27. Although the precise actions of. At excitatory synapses activation of presynaptic GABA B receptors causes a reduction of neurotransmitter release 15 by inhibiting voltage-dependent Calcium channels 16 17.
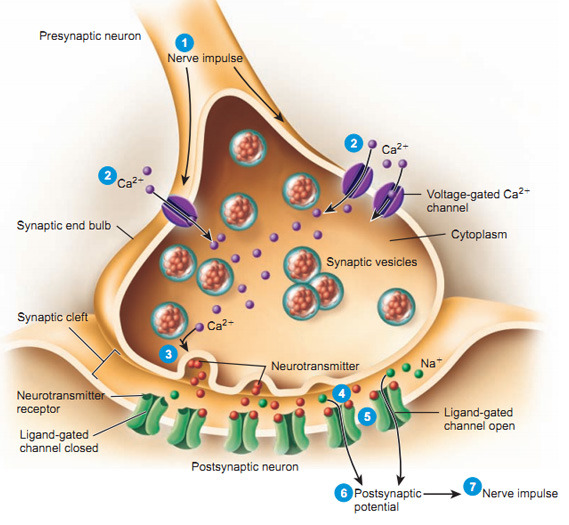 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Although the precise actions of. After spinal cord injury SCI the supraspinal control of primary afferent depolarization PAD interneurons is disengaged suggesting an increased role for. The amplitude of EPSPs in 15 soleus motoneurons was decreased by 5-84 with a mean inhibition. Presynaptic inhibition of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 TRPV1 receptors by noradrenaline in nociceptive neurons. Presynaptic inhibition of EPSPs was produced by trains of conditioning volleys in the posterior biceps-semitendinosus PBST nerve.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Presynaptic inhibition is modulated by supraspinal centres and primary afferents in order to filter sensory information adjust spinal reflex excitability and ensure smooth movement. As a result the information flowing through sensory terminals can be modified before it reaches the target neurones through a process that can be controlled selectively by supraspinal centres to optimise motor performance and sensory. Post-synaptic cells have mechanisms to communicate with the pre-synaptic cell and this can include inhibiting that cell. Although the precise actions of. When this occurs the inhibition is actually due to less excitatory input.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title presynaptic inhibition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






